Leave Your Message
In today's rapidly evolving digital landscape, Enterprise Routers play a crucial role in network management. According to a recent report by Frost & Sullivan, the global enterprise router market is expected to reach approximately $19 billion by 2025. This growth highlights the increasing demand for efficient data transmission and connectivity among businesses.
Enterprise Routers are specialized devices designed to manage and direct network traffic within an organization. They ensure that data packets reach their intended destinations securely and swiftly. However, companies often overlook the importance of selecting the right routers, leading to potential network inefficiencies. A study by Gartner indicates that 70% of enterprises experience network performance issues due to inadequate infrastructure.
Organizations must continuously assess their networking needs as technology advances. While Enterprise Routers provide essential functions, they may also introduce complexities that require careful consideration. Balancing performance and cost is a challenge many face, pushing them to rethink their strategies. Understanding the intricacies of Enterprise Routers is not just a technical requirement but a business imperative.

An enterprise router is a sophisticated networking device. It connects various networks and manages data traffic within large organizations. Unlike basic routers, enterprise routers support advanced features. They often prioritize performance, security, and scalability. These routers facilitate communication between branch offices, data centers, and the internet.
When it comes to functionality, enterprise routers provide various services. They include Virtual Private Network (VPN) support and quality of service (QoS) mechanisms. These features help ensure secure and optimal data transmission. In a world increasingly reliant on cloud services, performance becomes crucial. Such routers manage bandwidth effectively, minimizing latency. This optimization is essential for heavy data users in enterprises.
**Tip:** Regularly update your router’s firmware. This can enhance security and improve performance.
Enterprise routers may seem complex. However, their configuration can be straightforward with the right guidance. Documentation is often available, yet it may not cover every scenario. Testing may reveal shortcomings in setup or functionality. Frequent checks can help identify potential issues before they affect the network.
**Tip:** Keep monitoring the router logs. These logs provide insight into performance and potential issues. This habit can save time and trouble later on.
| Feature | Description | Benefits | Typical Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| High Throughput | Supports multiple data streams with minimal latency. | Ensures fast and efficient data transmission suitable for large organizations. | Data centers, large office networks. |
| Advanced Security Features | Integrated firewalls, VPN support, and threat detection. | Protects sensitive data and ensures compliance with regulations. | Corporate environments, remote work setups. |
| Scalability | Ability to add or remove resources as needed. | Supports growth without complete infrastructure overhaul. | Expanding businesses, dynamic workforces. |
| Multi-Protocol Support | Handles various networking protocols such as OSPF, BGP. | Flexibility in network design and interoperability with existing systems. | Complex enterprise networks, hybrid cloud setups. |
Enterprise routers play a critical role in large organizations. They facilitate the flow of data between different networks. Key components include interfaces, processors, and memory. Interfaces manage connections, allowing data to enter and exit. High-performance processors handle routing decisions swiftly, ensuring minimal latency. Memory stores routing data and crucial information for operations.
Companies often overlook the importance of redundancy in routers. If one component fails, traffic can be disrupted. Reports suggest that over 20% of network downtime is due to router failures. Utilizing redundant systems can significantly mitigate this risk.
Another vital aspect is security. Enterprise routers often come equipped with features for network security. Firewalls and intrusion detection systems help protect sensitive data. However, many organizations fail to update these configurations, leaving vulnerabilities. Regular audits and updates are essential for maintaining security.
Tips: Ensure your routers are equipped with the latest firmware updates. Network assessments can help identify potential weaknesses. Investing in training for IT staff will pay off in the long run.

Enterprise routers play a vital role in modern networks. They direct data traffic between different networks and ensure efficient communication. These routers handle numerous data packets simultaneously, optimizing performance and reliability. The process involves forwarding data based on IP addresses. Each packet travels through various paths to reach its destination. This routing process is crucial for seamless connectivity.
In a typical network, enterprise routers analyze incoming data. They determine the best route for each packet. This decision-making process takes into account network congestion and speed. The routers adapt to changing network conditions. For example, if one path is slow, the router reroutes traffic through a faster one. This dynamic rerouting capability is essential for maintaining high performance.
However, not all enterprise routers function perfectly all the time. Misconfigurations may lead to slowdowns or data loss. Network managers must regularly check settings and performance metrics. Identifying and fixing these issues can be a challenge. Continuous monitoring allows for adjustments and enhancements, ensuring the network runs smoothly. Reflecting on these aspects highlights the complexity and importance of enterprise routers in today’s business landscape.
Enterprise routers play a critical role in managing data traffic across large organizations. They handle multiple connections and protocols, ensuring efficient communication. According to a recent industry report, approximately 75% of businesses see improved network performance after implementing enterprise routers. This leads to faster data transmission and reduced latency.
The benefits of using enterprise routers extend beyond mere speed. Enhanced security protocols are often integrated, protecting sensitive data during transit. With cyber threats on the rise, a 2022 survey revealed that 68% of IT professionals consider secure routing a priority. Effective routers also allow for better network scalability. As businesses grow, their routing needs change significantly. A flexible router can adapt to these shifts with ease.
However, there are challenges in adopting enterprise routers. Proper configuration is essential. A misconfiguration can lead to vulnerable points in the network. Additionally, the complexity of these devices often requires specialized knowledge that not all organizations possess. This gap could lead to inefficiencies. Investing in training or consulting services is essential for configuring and maintaining these systems effectively. The benefits are substantial, but the need for reflection on management practices remains critical.
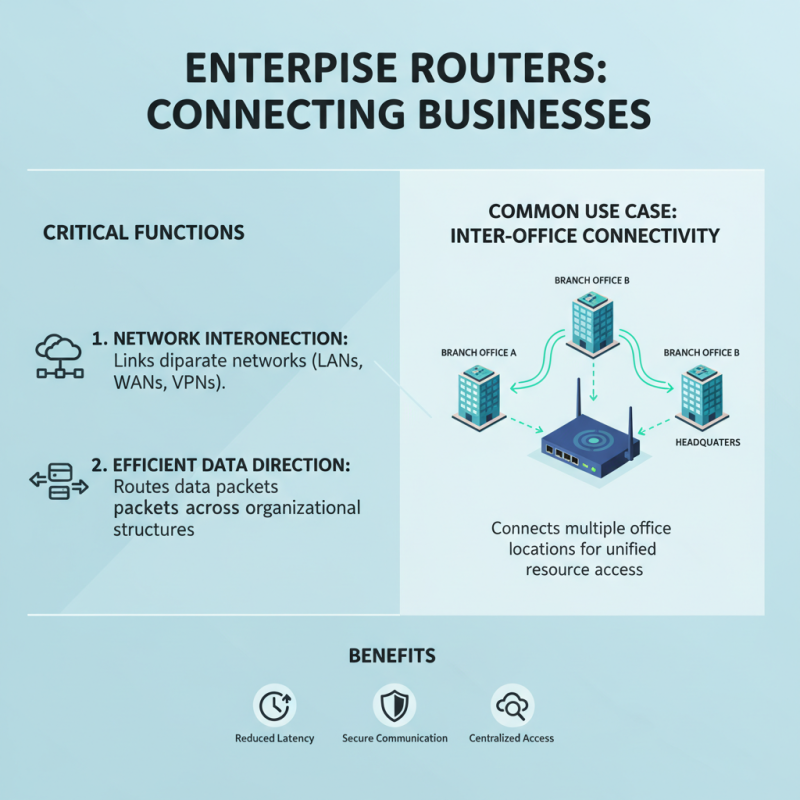
Enterprise routers serve critical functions in business environments. They connect various networks, directing data efficiently across organizational structures. One common use case is interconnecting different office locations. Businesses often have multiple branches. An enterprise router enables seamless communication between these sites, ensuring that employees can access centralized resources without delays.
Another significant application is managing large amounts of traffic. In organizations with high data demands, routers prioritize traffic effectively. This helps avoid bottlenecks, improving overall performance. Many companies utilize Quality of Service (QoS) features. These features ensure that essential applications receive the bandwidth they need. Yet, configuring these settings can be challenging. Misconfigurations may lead to unintended failures in application performance.
Security is also a key use case. Routers have built-in firewalls and VPN capabilities. This prevents unauthorized access and protects sensitive information. However, enterprise routers must be updated regularly. Old firmware can expose vulnerabilities. Many businesses struggle to keep up with these updates. Balancing security and functionality is not always straightforward.
